Runtime Configuration¶
A runtime configuration provides Elyra access to external resources, such as a Kubeflow Pipelines deployment. You can manage runtime configurations using the JupyterLab UI or the Elyra CLI.
Prerequisites¶
A Kubeflow Pipelines runtime configuration requires connectivity details for
- A Kubeflow Pipelines deployment
- S3-based Object Storage (e.g. minio or IBM Cloud Object Storage)
Managing runtime configurations using the JupyterLab UI¶
To create, edit, or delete runtime configurations using the UI select the Runtimes tab from the JupyterLab sidebar.
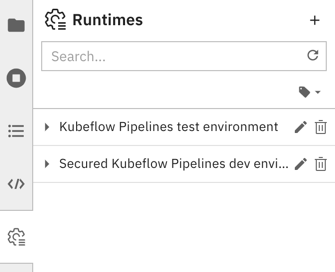
Creating a runtime configuration¶
To create a runtime configuration for a Kubeflow Pipelines deployment:
Select the
Runtimestab from the JupyterLab sidebar.Click
+to add a new runtime configuration.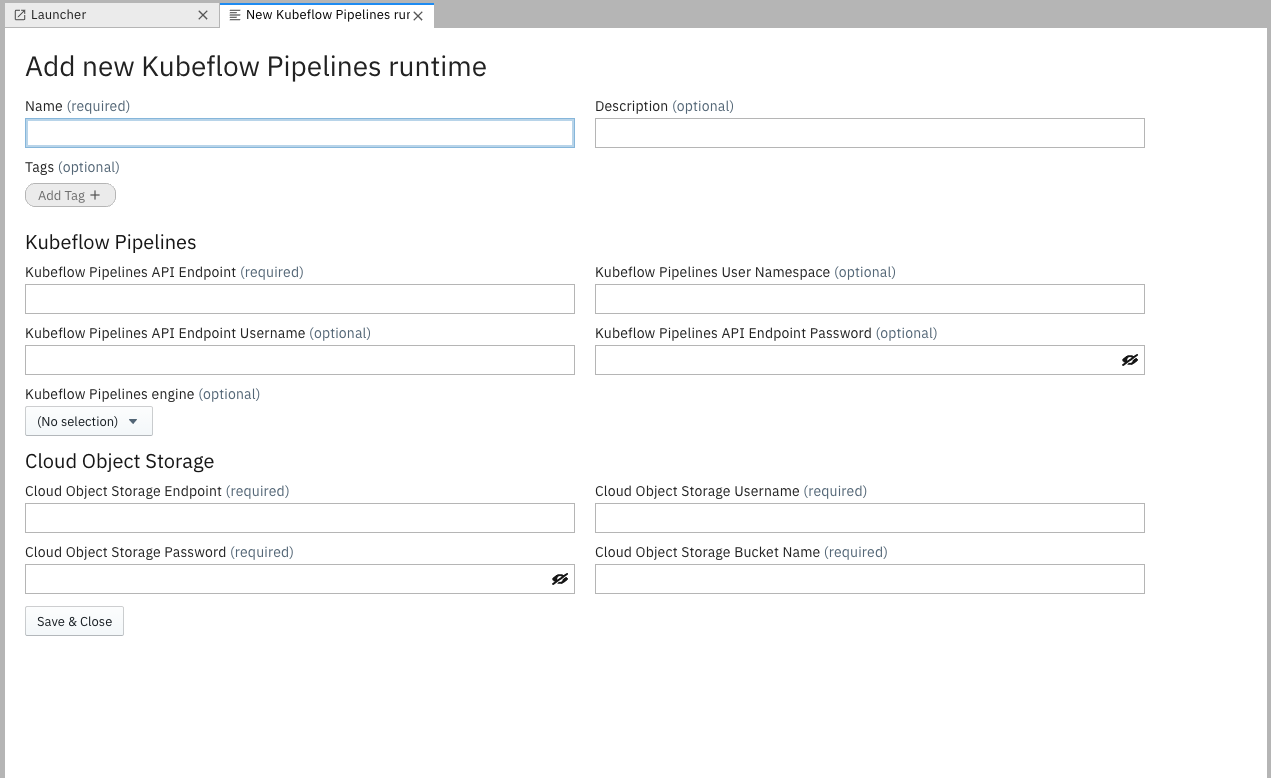
Provide a runtime display name, an optional description, and tag the configuration to make it more easily discoverable.
Enter the Kubeflow Pipelines and Cloud Storage connectivity information. Refer to section Configuration settings for details.
Save the runtime configuration. The new entry is displayed in the list.
Expand the entry and verify that you can access the Kubeflow Pipelines UI and the Cloud Storage UI using the displayed links.
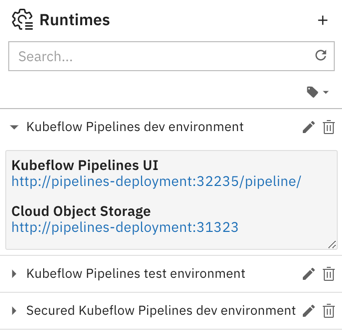
Modifying a runtime configuration¶
To edit a runtime configuration for a Kubeflow Pipelines deployment:
- Select the
Runtimestab from the JupyterLab sidebar. - Click the pencil next to the runtime configuration.
Deleting a runtime configuration¶
To delete a runtime configuration for a Kubeflow Pipelines deployment:
- Select the
Runtimestab from the JupyterLab sidebar. - Click the trash can next to the runtime configuration.
Managing runtime configurations using the Elyra CLI¶
You can list, create, edit, or delete runtime configurations using the elyra-metadata CLI.
Listing runtime configurations¶
To list runtime configurations run
elyra-metadata list runtimes
The output lists for each runtime the name and the name of the associated JSON formatted metadata file, which is stored in the JupyterLab data directory in the metadata/runtimes subdirectory.
Available metadata instances for runtimes (includes invalid):
Schema Instance Resource
------ -------- --------
kfp my_kfp /Users/jdoe/Library/Jupyter/metadata/runtimes/my_kfp.json
To format the output as JSON run elyra-metadata list runtimes --json. Note that the JSON export includes the content of the metadata files, not just their names.
Creating a runtime configuration¶
To create a runtime configuration for a Kubeflow Pipelines deployment:
elyra-metadata install runtimes \
--display_name="My Kubeflow Pipelines Runtime" \
--api_endpoint=https://kubernetes-service.ibm.com/pipeline \
--api_username=username@email.com \
--api_password=mypassword \
--engine=Argo \
--cos_endpoint=http://minio-service.kubeflow:9000 \
--cos_username=minio \
--cos_password=minio123 \
--cos_bucket=test-bucket \
--tags="['kfp', 'v1.0']"
Refer to section Configuration settings for an explanation of the parameters.
Modifying a runtime configuration¶
To edit a runtime configuration:
elyra-metadata install runtimes \
--replace \
--name="my_kubeflow_pipelines_runtime" \
--display_name="My Kubeflow Pipelines Runtime" \
--api_endpoint=https://kubernetes-service.ibm.com/pipeline \
--api_username=username@email.com \
--api_password=mynewpassword \
--engine=Argo \
--cos_endpoint=http://minio-service.kubeflow:9000 \
--cos_username=minio \
--cos_password=minio123 \
--cos_bucket=test-bucket \
--tags="['kfp', 'v1.1']"
Refer to section Configuration settings for an explanation of the parameters. Note that you must specify the --name parameter.
Deleting a runtime configuration¶
To delete a runtime configuration run the following command, replacing the configuration name as appropriate.
elyra-metadata remove runtimes --name=my_kubeflow_pipelines_runtime
Configuration settings¶
Runtime configuration settings¶
This section defines the runtime configuration settings.
display_name¶
A user-friendly name for the runtime configuration. This setting is required.
Example: Kubeflow Pipelines dev environment
name¶
A unique identifier for this configuration. A value is automatically generated from display_name.
Example: kubeflow_pipelines_dev_environment
description¶
A user-friendly description for this runtime configuration.
Example: Kubeflow Pipelines deployment in QA
Kubeflow Pipelines settings¶
This section defines the settings for the Kubeflow Pipelines deployment that you want to associate with this runtime configuration.
api_endpoint¶
The KubeFlow Pipelines API endpoint you want to utilize. This setting is required.
Example: https://kubernetes-service.ibm.com/pipeline
user_namespace¶
The namespace used to run your pipeline in Kubeflow Pipelines. This setting is required if the Kubeflow Pipelines deployment is multi-user, auth enabled. SEE NOTE.
Example: mynamespace
api_username¶
Username used to access your KubeFlow Pipelines API endpoint. This setting is required if the Kubeflow Pipelines deployment is multi-user, auth enabled. SEE NOTE.
Example: username@email.com
api_password¶
Password used to access your KubeFlow Pipelines API endpoint. This setting is required if the Kubeflow Pipelines deployment is multi-user, auth enabled. SEE NOTE.
Example: mypassword
engine¶
The engine being used by Kubeflow Pipelines: Argo or Tekton (default is Argo).
Example: Argo
Cloud Storage settings¶
This section defines the settings for the cloud storage that you want to associate with this runtime configuration.
cos_endpoint¶
This should be the URL address of your S3 Object Storage. If running an Object Storage Service within a Kubernetes cluster (Minio), you can use the Kubernetes local DNS address. This setting is required
Example: https://minio-service.kubeflow:9000
cos_username¶
Username used to access the Object Store. This setting is required. SEE NOTE.
Example: minio
cos_bucket¶
Name of the bucket you want your artifacts in. This setting is required. If the bucket doesn’t exist, it will be created. The specified bucket name must meet the naming conventions imposed by the object storage service.
Example: test-bucket
Note: If using IBM Cloud Object Storage, you must generate a set of HMAC Credentials
and grant that key at least Writer level privileges.
Your access_key_id and secret_access_key will be used as your cos_username and cos_password respectively.
Troubleshooting¶
I am seeing this error when using Elyra with Kubeflow Pipelines that is Dex enabled:
HTTP response body: {"error":"Validate experiment request failed.: Invalid input error: Invalid resource references for experiment. Expect one namespace type with owner relationship.
- Ensure that you have logged into the Kubeflow dex landing page (https://kubeflow.cluster:31380….) at least once with your credentials via the UI. You should have been greeted with a dialog box and request to create a new namespace. Without this step complete, Elyra will not be able to create pipelines on the Kubeflow cluster.
- Ensure your credentials in the
runtimessection of Elyra is accurate and up to date. Ensure thatuser_namespace,api_usernameandapi_passwordare all filled out. When using Dex, theapi_usernameis typically your email address anduser_namespaceis your email shortname (elyra if elyra@email.org)